Hurricane Formation and Tracking: Hurricane Tracker
![]()
Hurricane tracker – Hurricanes are among the most powerful and destructive forces of nature, capable of causing widespread damage and loss of life. Understanding how hurricanes form and how to track their paths is crucial for mitigating their impact and ensuring public safety.
With the hurricane season upon us, it’s crucial to stay informed about potential storms. The National Hurricane Center provides a comprehensive hurricane tracker that allows you to monitor storm paths and intensities. Interestingly, the tracker recently showed a storm approaching Colorado, a state known for its mountains rather than coastal waters.
This unusual occurrence has sparked discussions among meteorologists and has even caught the attention of lauren boebert , a controversial Republican congresswoman from the state. As the storm continues to move inland, the hurricane tracker remains an invaluable tool for tracking its progress and ensuring the safety of those in its path.
Meteorological Conditions for Hurricane Formation
Hurricanes are formed over warm ocean waters, typically at temperatures of at least 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27 degrees Celsius). The warm water provides the energy that drives the hurricane’s development. Other meteorological conditions that contribute to hurricane formation include:
- Low wind shear: Wind shear is the difference in wind speed and direction between two levels of the atmosphere. Low wind shear allows hurricanes to maintain their vertical structure and prevents them from being torn apart.
- High humidity: Hurricanes need moisture to form and sustain themselves. High humidity provides the water vapor that condenses into clouds and rain.
- Coriolis effect: The Coriolis effect is a force that deflects objects moving in the Earth’s atmosphere. This force causes hurricanes to rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Stages of Hurricane Development
Hurricanes develop through several stages, each with its own characteristics:
- Tropical depression: A tropical depression is a low-pressure area with organized thunderstorms and sustained winds of less than 39 miles per hour (63 kilometers per hour).
- Tropical storm: A tropical storm is a tropical depression with sustained winds of 39 to 73 miles per hour (63 to 118 kilometers per hour).
- Hurricane: A hurricane is a tropical storm with sustained winds of 74 miles per hour (119 kilometers per hour) or higher.
Hurricane Tracking, Hurricane tracker
Tracking hurricanes is essential for predicting their paths and issuing timely warnings. Various methods are used to track hurricanes, including:
- Weather satellites: Weather satellites provide real-time images of hurricanes, allowing meteorologists to monitor their development and movement.
- Aircraft reconnaissance: Aircraft fly into hurricanes to collect data on their wind speed, pressure, and other meteorological conditions.
- Buoys: Buoys are deployed in the ocean to collect data on wave height, wind speed, and other oceanographic conditions.
- Computer models: Computer models are used to predict hurricane paths and intensity based on data from weather satellites, aircraft reconnaissance, and buoys.
Hurricane Impact and Preparedness

Hurricanes are powerful storms that can cause widespread devastation. They can produce high winds, storm surge, and flooding, which can damage homes and businesses, and even cause loss of life. It is important to be prepared for hurricanes, and to know what to do to stay safe during a hurricane.
Potential Impacts of Hurricanes
The potential impacts of hurricanes can be significant. These impacts include:
- Storm surge: Storm surge is a wall of water that can be as high as 20 feet or more. It can cause severe flooding and damage to coastal areas.
- Flooding: Hurricanes can also cause flooding from heavy rains. This flooding can damage homes and businesses, and can also make it difficult to get around.
- Wind damage: Hurricanes can produce high winds that can damage homes, businesses, and other structures. These winds can also cause trees and power lines to fall, which can create additional hazards.
Hurricane Preparedness
It is important to be prepared for hurricanes. There are a number of things you can do to prepare, including:
- Develop an evacuation plan: In the event of a hurricane, it is important to have an evacuation plan in place. This plan should include a list of places you can go if you need to evacuate, as well as a list of contacts you can reach out to for help.
- Assemble an emergency kit: An emergency kit is a collection of supplies that you can use in the event of a hurricane. This kit should include items such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
- Stay informed: It is important to stay informed about hurricanes. You can do this by listening to the radio, watching the news, or checking the internet.
Staying Safe During a Hurricane
If you are in the path of a hurricane, there are a number of things you can do to stay safe. These include:
- Stay indoors: The safest place to be during a hurricane is indoors. If you are in a sturdy building, stay inside and away from windows.
- Stay away from floodwaters: Floodwaters can be dangerous and can contain harmful bacteria. Avoid walking or driving through floodwaters.
- Be aware of downed power lines: Downed power lines can be dangerous and can cause electrocution. If you see a downed power line, stay away from it and call 911.
Hurricane Data and Visualization
During hurricane tracking, various types of data are collected to provide comprehensive information about the storm’s behavior and intensity. These include:
Wind Speed
Wind speed is a crucial parameter in hurricane tracking. It is measured using instruments such as anemometers and radar systems. Wind speeds are categorized according to the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, which ranges from Category 1 (74-95 mph) to Category 5 (157 mph or higher).
Pressure
Atmospheric pressure is another important indicator of hurricane intensity. Low pressure at the storm’s center signifies a stronger hurricane. Pressure readings are obtained from weather stations, buoys, and satellites.
Rainfall
Rainfall data is essential for assessing the potential flooding hazards associated with hurricanes. Rainfall amounts are measured using rain gauges and radar systems. Heavy rainfall can lead to flash flooding, riverine flooding, and other water-related hazards.
Data Visualization
Data visualization tools are indispensable for tracking and analyzing hurricane activity. These tools allow meteorologists and emergency managers to visualize and interpret complex data sets, enabling them to make informed decisions and provide timely warnings.
Some common data visualization techniques used in hurricane tracking include:
- Satellite imagery: Satellite images provide a broad view of the storm’s structure, movement, and intensity.
- Radar data: Radar data provides detailed information about the storm’s precipitation patterns and wind speeds.
- Numerical weather models: Computer models simulate hurricane behavior and predict their future tracks and intensities.
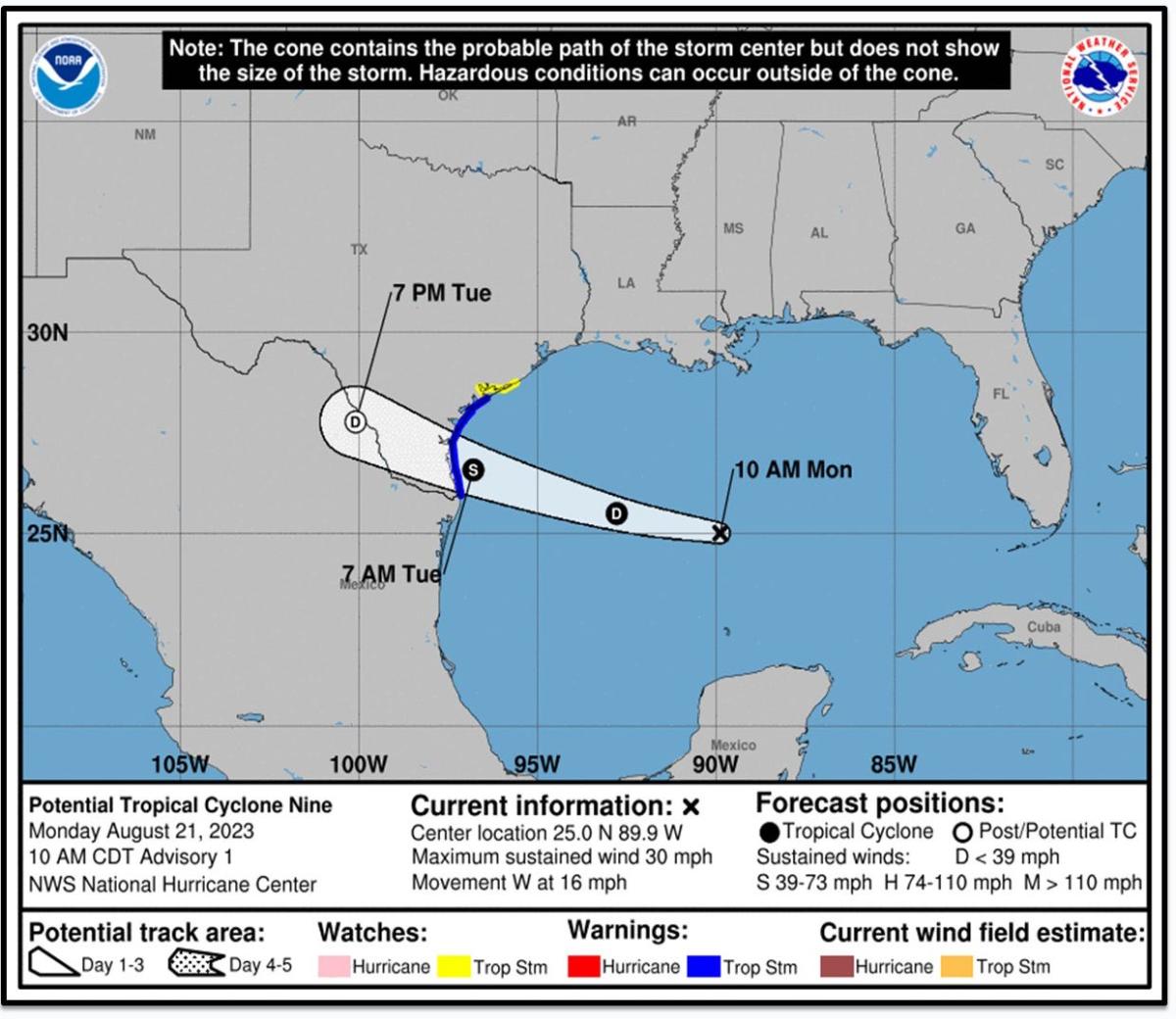
- Hurricane track maps: These maps show the projected path of the hurricane and its intensity over time.
Hurricane Data Table
The following table provides a summary of key hurricane data:
| Hurricane Name | Category | Wind Speed (mph) | Projected Path |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hurricane Ian | Category 4 | 155 | Florida Gulf Coast |
| Hurricane Fiona | Category 3 | 115 | Eastern Canada |
| Hurricane Julia | Category 1 | 85 | Central America |
Amidst the swirling winds and torrential downpours, the hurricane tracker stood sentinel, its gaze fixed on the tempestuous waters. As the storm raged, a beacon of hope emerged in the form of Jamaal Bowman , a voice of resilience and unity.
Like the hurricane tracker, he navigated the treacherous waters of adversity, guiding his community through the tempestuous seas of social and economic challenges. With unwavering determination, he steered them towards a brighter horizon, leaving an enduring legacy that would forever be etched in the annals of their history.